In our February Short-Term Energy Outlook (STEO), we forecast that U.S. refinery utilization will remain similar to 2022 at above 90% over the next two years. The industry is returning to more typical rates after low refinery utilization in 2020 and 2021. We forecast U.S. refinery utilization will average 90.8% in 2023 and then decrease slightly to 90.3% in 2024.
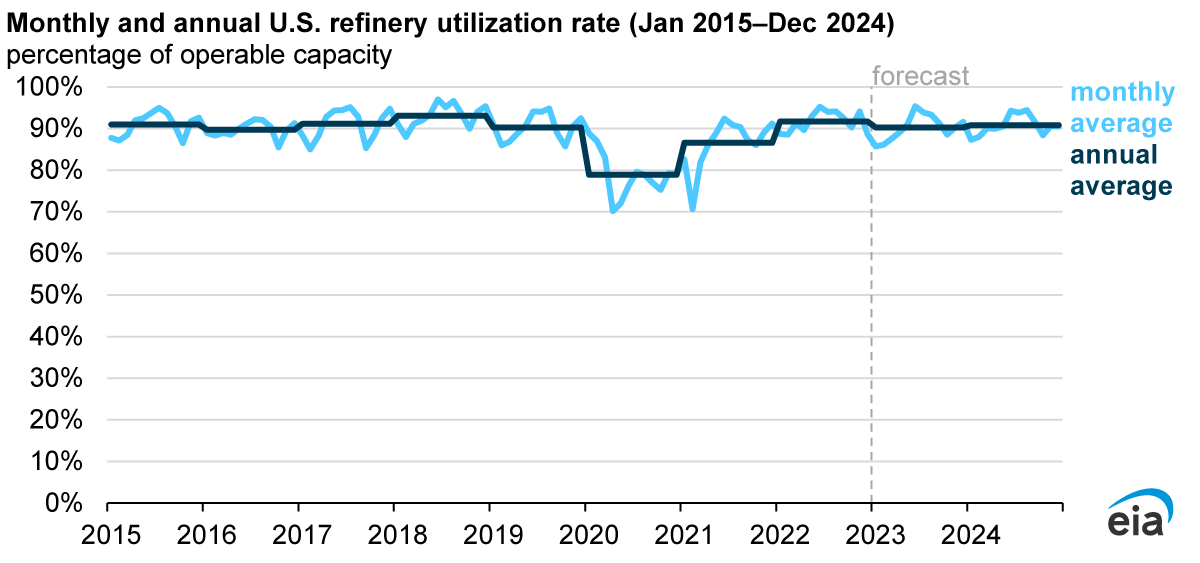
Refinery utilization is the amount of crude oil and other oils used as input at a refinery divided by the total capacity at that refinery. In 2020, average refinery utilization dropped to 78.8%, the lowest annual rate since we began collecting this data in 1997, but by 2022, utilization rates averaged closer to pre-pandemic levels at more than 91%. On an annual average basis, fleet-wide refinery utilization rarely climbs much higher than 95% because of maintenance periods and seasonal periods of less demand.
We expect petroleum product prices for gasoline and diesel will be lower in 2023 than in 2022. Nevertheless, petroleum product prices in 2023 will remain high compared with pre-pandemic prices, especially as refiners undergo maintenance in the spring. Low spring utilization will limit production before the summer and encourage refineries to maintain high utilization during the summer and when not undergoing maintenance.
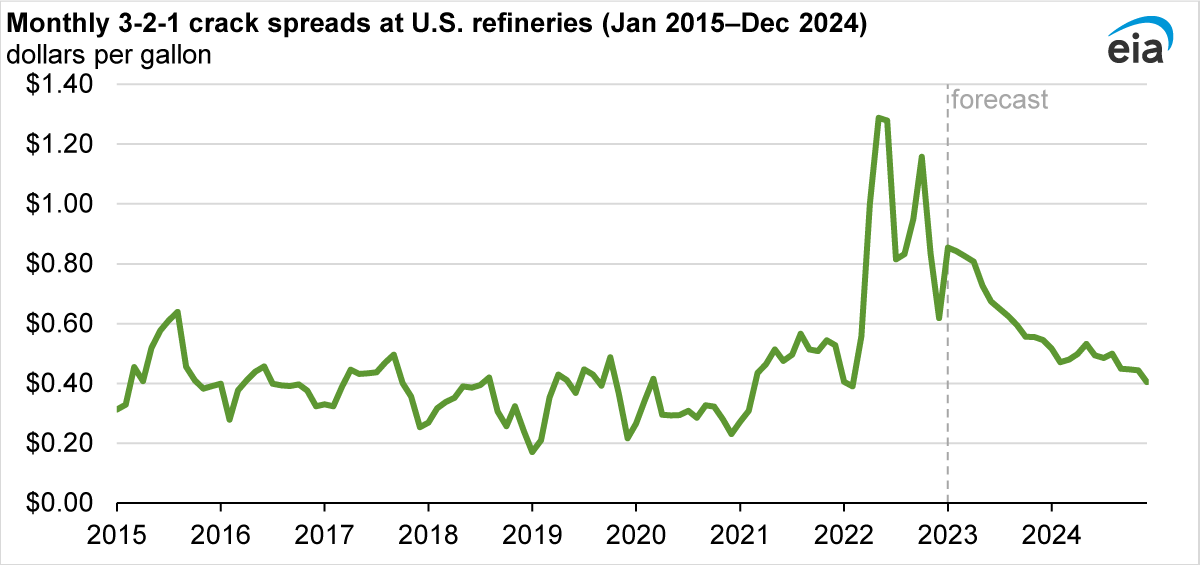
Note: The 3-2-1 crack spread is calculated by subtracting the value of a gallon of Brent crude oil (based on the Brent spot average) from the price of two-thirds of a gallon of gasoline and one-third of a gallon of diesel (based on the refiner price for resale).
We expect slower economic growth in 2023 and 2024, which would reduce gasoline and diesel consumption compared with 2022, leading to a gradual decrease in petroleum product prices. We also forecast that increased production of finished petroleum products as a result of high refinery utilization rates will contribute to lower prices. The ban on imports of refined petroleum products from Russia into the EU, which began earlier this month, poses a risk of additional disruptions and brings significant uncertainty to our forecast.
Principal contributor: Kevin Hack









