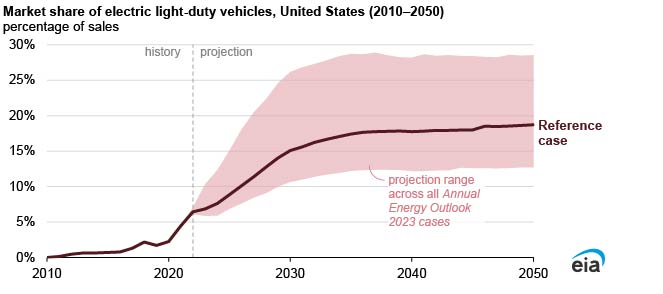
According to the EIA’s Annual Energy Outlook 2023 (AEO2023), they project that electric vehicles (EVs), including both battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), will account for between 13% and 29% of new light-duty vehicle sales in the United States in 2050 and between 11% and 26% of on-road light-duty vehicle stocks. Declines in EV component costs, along with federal and state policies that provide incentives for EV purchases or require minimum sales, drive EV sales growth in our model projection.
In its AEO2023, the EIA explores long-term energy trends in the United States and present an outlook for energy markets through 2050. They use different scenarios, called cases, to understand how varying assumptions affect energy trends. The AEO2023 Reference case, which serves as a baseline, or benchmark, case, reflects laws and regulations adopted through mid-November 2022, including the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).
The decision to purchase an EV can be affected by many considerations, and purchase price is among the most important. The EIA model breaks the light-duty passenger vehicle market into 16 size classes—eight car and eight light truck—and estimates average EV purchase prices for each. They project that EV purchase prices will continue to decrease and that most EVs with less than a 150-mile driving range could reach purchase price parity with conventional gasoline-powered vehicles by 2029. EVs with between 151 miles and 250 miles of driving range reach price parity across most car size classes by 2038, while among light trucks, only small van and small crossover utility vehicle (CUV) size classes reach cost parity. EVs with over 250 miles of range do not reach price parity in any size class but approach it in the 2040s; car size classes are all within 3% of the respective gasoline vehicle purchase price, and most light truck size classes are within 5%. Initial EV buyers have demonstrated a willingness to pay for long range EVs, but whether this behavior will be demonstrated by the majority of new light-duty vehicle buyers remains uncertain.
The EIA assumes the currently enacted Corporate Average Fuel Economy standards, which apply to model years 2023–26, result in technological improvements and increased EV adoption because of declining cost and favorable fuel economy credits. This change occurs in parallel with continued increases in fuel economy for conventional gasoline-powered vehicles. Our model also ensures legally enforceable state minimum EV sales requirements are met. For example, California’s Advanced Clean Cars rule (last modified in 2016) has been adopted by 15 additional states through Section 177 of the Clean Air Act. The EIA adjusts EV purchase prices to account for the Clean Vehicle Credit implemented in the IRA, using official U.S. government forecast expenditures to estimate the number of EVs that will be eligible through the lifetime of the regulation.
Significant uncertainties are inherent to projecting the rate at which electric vehicles will become more common in the light-duty vehicle market. Some important variables include:
• Future policies, including emissions and fuel economy regulations as well as vehicle sale mandates or combustion engine bans
• Disruptive technological advancements
• Availability and access to refueling infrastructure
• Consumer attitudes and behavior
• Critical mineral supply chains
Given inherent interest in EVs and the role vehicle electrification could play in meeting greenhouse emission reductions, the EIA expects near- and mid-term market dynamics, while uncertain at this time, will be critical to the rate of EV adoption. The EIA continuously monitor vehicle markets, technology developments, and policy changes and update our models as needed to ensure that we capture anticipated market conditions.









