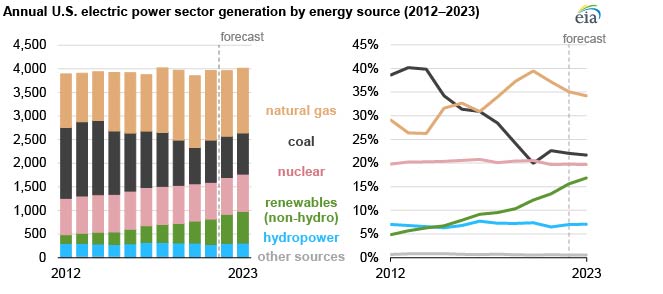
In our January Short-Term Energy Outlook (STEO), we forecast that rising electricity generation from renewable energy resources such as solar and wind will reduce generation from fossil fuel-fired power plants over the next two years. The forecast share of generation for U.S. non-hydropower renewable sources, including solar and wind, grows from 13% in 2021 to 17% in 2023. We forecast that the share of generation from natural gas will fall from 37% in 2021 to 34% by 2023 and the coal share will decline from 23% to 22%.
One of the most significant shifts in the mix of U.S. electricity generation over the past 10 years has been the rapid expansion of renewable energy resources, especially solar and wind. The amount of solar power generating capacity operated by the U.S. electric power sector at the end of 2021 is 20 times more than it was at the end of 2011, and U.S. wind power capacity is more than twice what it was 10 years ago.
In our current STEO, we forecast that most of the growth in U.S. electricity generation in 2022 and 2023 will come from new renewable energy sources. We estimate that the electric power sector had 63 gigawatts (GW) of existing solar power generating capacity operating at the end of 2021. We forecast solar capacity will grow by about 21 GW in 2022 and by 25 GW in 2023. We expect that 7 GW of wind generating capacity will be added in 2022 and another 4 GW in 2023. Operating wind capacity totaled 135 GW at the end of 2021.
Our forecast of growth in renewable electricity generation over the next two years leads to our forecast of a reduced need for fossil-fueled generation. Although we expect natural gas prices for electric generators to decline, the operating costs of renewable generators will continue to be generally lower than natural gas-fired units. We expect that regions of the country with the largest increases in renewable capacity, such as Texas and the Midwest/Central regions, will experience the largest reductions in natural gas generation.











